As companies expand, managing essential revenue processes like billing, receivables, revenue recognition, and payments becomes increasingly complex. This guide will explore the transformative impact of a new category of software known as revenue automation (RA), which enhances efficiency, reduces manual tasks, and improves compliance. Whether it involves complex invoicing or payment processing, revenue automation can fundamentally change how your business operates.
In this guide, you’ll learn:
- What revenue automation is
- Key benefits
- Why revenue automation is critical now
- Which companies benefit most
- How revenue automation works
- Core capabilities
- How it differs from other software categories
- Real-life transformations achieved with revenue automation software
- Common adoption concerns
- Steps to implement
By the end of this guide, you’ll see how revenue automation can provide a competitive advantage, setting your company up for sustained growth and increased efficiency.
Let's jump in!
Introduction
In today's fast-evolving business landscape, efficient and accurate revenue management is crucial. As businesses grow, they often surpass the capabilities of traditional systems like Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) tools and Customer Relationship Management (CRM) software. Manual processes, fragmented workflows, and outdated systems not only decelerate operations but also pose significant risks and inefficiencies. Revenue automation offers a groundbreaking approach to enhance the entire revenue cycle—from the closure of deals to financial reporting and audits.
Revenue automation serves as a strategic framework, not merely a tool, addressing the specific demands of revenue-focused activities. While ERP systems are proficient at broad business management and ensuring accounting compliance, they frequently fall short in areas like billing, payments, and revenue recognition, lacking the necessary visibility for strategic business reporting. RA software bridges this gap with a unified platform that automates these critical functions, ensuring accuracy, compliance, and efficiency throughout. Its seamless integration with existing systems enhances rather than disrupts your operations, making RA a vital component of any modern financial strategy.
As we delve into RA’s components—from data capture to invoicing and integrations—you'll see how it converts labor-intensive processes into streamlined, automated workflows. We'll also compare RA with other software types, such as CRMs, billing tools, and BI reporting platforms, to demonstrate how RA uniquely addresses the complexities of revenue management. Real-world examples and case studies will illustrate how various industries leverage RA to boost efficiency, cut costs, and enhance financial outcomes.
However, adopting RA involves more than just new software installation; it's about preparing your business for a future shaped by dynamic revenue models, such as subscriptions or usage-based pricing. This guide will walk you through assessing your current revenue workflows, implementing an RA platform, and optimizing its use for continuous success. You'll learn to navigate common objections and challenges, ensuring a smooth transition to RA.
This guide aims to provide a thorough understanding of revenue automation and its implementation within your company. Whether you lead a growing software firm, a services company with diverse billing needs, or a large enterprise managing complex customer interactions, RA offers a route to greater efficiency, accuracy, and scalability. As we explore RA’s future, you will understand how this technology is poised to become a cornerstone of modern business operations, enabling companies to confidently handle the complexities of the digital economy.
What is revenue automation?
Revenue automation represents a breakthrough in software technology, specifically designed to streamline and automate the entire revenue cycle for SaaS and service-based businesses—from contract initiation to financial reporting. RA transcends traditional ERP systems, which typically focus on core accounting functions and often require manual intervention.
Instead, RA provides a comprehensive platform that enhances revenue operations like complex invoicing, receivables collection, and compliance with standards such as ASC 606. By integrating seamlessly with existing ERP systems, RA not only eliminates manual processes and reduces errors but also accelerates financial closing and boosts overall operational efficiency.
What are the business benefits of RA?
Implementing Revenue Automation offers a multitude of advantages that streamline operations and enhance organizational effectiveness. RA automates intricate tasks, significantly reducing manual effort and the potential for errors, which leads to quicker financial closings and robust reporting. Its cohesive platform replaces disparate systems, improving scalability and ensuring compliance with critical accounting standards like ASC 606. Here are the key benefits:
- Increased Efficiency: Automates routine tasks, freeing up time for strategic initiatives.
- Faster Financial Close: Accelerates the month-end closing process, enabling more timely financial decision-making.
- Reduced Errors: Decreases the likelihood of human error in billing and revenue recognition through automation.
- Scalability: Efficiently manages increasing business volumes and complexity.
- Improved Cash Flow: Enhances the efficiency of invoicing and collections, speeding up receivables and bolstering cash management.
- Enhanced Compliance: Maintains rigorous adherence to accounting standards, mitigating the risk of compliance breaches.
- Unified Platform: Consolidates all revenue-related processes into one integrated solution, obviating the need for multiple systems.
- Better Visibility: Provides real-time insights into financial data, aiding in more accurate forecasting and strategic planning.
- Customer Satisfaction: Ensures invoices are accurate and issued promptly, fostering trust and minimizing disputes.
- Cost Savings: Lowers operational costs by reducing the need for manual interventions and multiple software solutions.
These benefits collectively enhance not only the operational throughput but also position businesses to better satisfy customer needs and adapt to market changes, thereby securing a competitive edge in the industry. Why is RA important right now?
In today’s dynamic business environment, relying on outdated, manual processes to manage revenue cycles is no longer viable. As businesses grow, the complexities of billing, invoicing, and revenue recognition escalate, making manual oversight not only cumbersome but also error-prone. Revenue automation is essential as it simplifies these processes, enabling companies to manage sophisticated revenue workflows efficiently and accurately. By automating tasks that traditionally required extensive manual effort, RA enhances operational efficiency and minimizes the risk of costly errors that could affect the bottom line.
Additionally, the financial landscape is increasingly regulated, with stringent standards like ASC 606 mandating strict compliance. Manual processes often fall short in meeting these requirements, exposing businesses to risks of non-compliance and potential penalties. RA addresses these challenges by ensuring all revenue-related activities conform seamlessly to current accounting standards. This safeguards businesses against regulatory risks and bolsters stakeholder confidence through precise, timely, and compliant financial reporting.
Furthermore, in an era dominated by data-driven decision-making, RA offers vital real-time insights that empower strategic planning. With RA, companies gain a comprehensive view of their financial data, enhancing forecasting, cash flow management, and long-term operational planning. Adopting RA positions businesses to stay ahead in a competitive market by optimizing revenue processes and laying a foundation for sustained growth. The advantages of RA are evident, making now the optimal time to embrace this transformative technology.
What kinds of companies benefit from RA?
RA is invaluable for rapidly growing software companies facing increasingly complex revenue processes as they scale. These companies typically experience a surge in customer volume, each with unique billing requirements. RA simplifies this complexity by automating invoicing, revenue recognition, and reporting processes, allowing software businesses to focus on innovation and growth rather than being hindered by manual revenue management tasks. By enhancing these processes, RA ensures that as the business expands, its financial operations remain efficient, precise, and scalable.
Companies pioneering new business models, such as subscription-based services or usage-based pricing, find significant advantages in using RA. These business models often involve complex and dynamic billing requirements needing frequent adjustments. RA offers the necessary flexibility to effortlessly manage these evolving revenue streams, ensuring robust support for a company's innovative offerings. This adaptability not only enables businesses to rapidly respond to market demands but also empowers them to explore and implement new revenue models without the limitations of conventional billing systems.
Service-oriented businesses, including consulting firms, professional services companies, and creative agencies, also greatly benefit from RA. These businesses often manage diverse billing scenarios—from bespoke contracts and variable billing cycles to project-based client work. RA streamlines these varied revenue streams by integrating billing, accounts receivable (AR), and revenue recognition into a unified, automated platform. This consolidation allows service businesses to keep their financial records accurate and consistent, improve cash flow, and enhance customer satisfaction with timely and precise invoicing.
How does revenue automation work?
RA operates through two primary layers that together streamline and automate the invoice-to-cash cycle for businesses, enhancing overall efficiency and accuracy.
Data Aggregation Layer: This foundational layer consolidates all essential data—customer details, financial transactions, invoices, and payments—into a single, unified system. By removing data silos and ensuring a cohesive data environment, this layer allows every RA platform module to access the same up-to-date and consistent information. This comprehensive data integration is crucial for maintaining accuracy across all revenue-related activities and serves as the backbone for effective automation.
Application Layer: Sitting on top of the data aggregation layer, the application layer comprises various interconnected modules tailored to automate specific aspects of the revenue management process. It encompasses everything from contract management and invoicing to payment processing, revenue recognition, and financial reporting. As these modules are fed from a singular data source, they function cohesively, ensuring that every component of the revenue process is aligned and synchronized. This unified approach not only minimizes the need for manual input but also significantly enhances the accuracy and scalability of business operations, allowing companies to grow without the burdens of managing disparate systems.
What are the core capabilities of an RA platform?
Data Capture
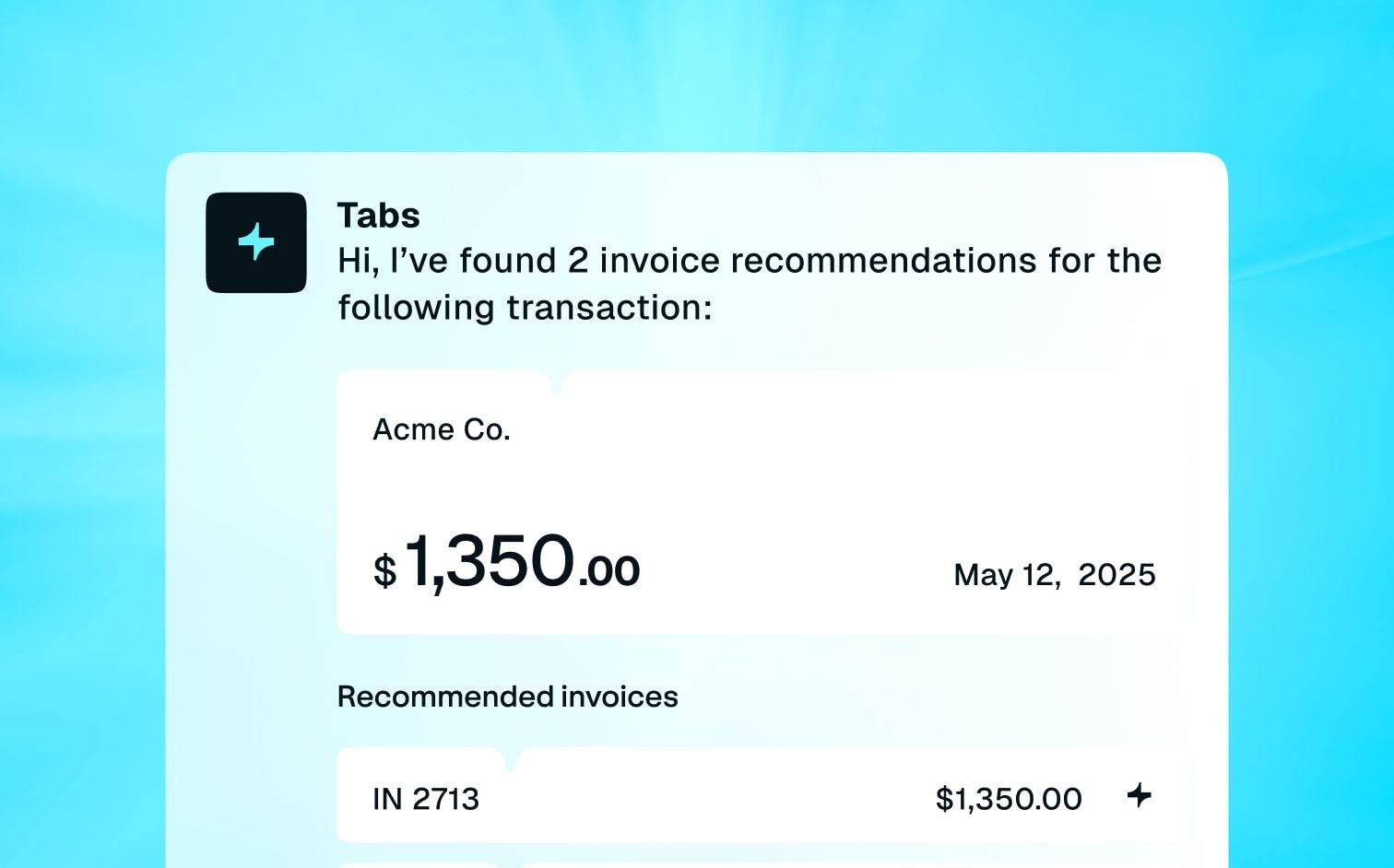
The Data Capture module serves as the foundation of revenue automation, utilizing advanced AI technologies, such as Computer Vision and Large Language Models (LLMs), to automatically process and extract vital information from key documents like contracts, purchase orders, and agreements. This automation streamlines data entry, minimizes errors, and ensures critical details such as pricing, terms, and billing schedules are accurately captured and integrated into the billing and revenue recognition workflows.
Invoicing
The Invoicing module enhances billing efficiency by automating the creation and distribution of invoices. It is capable of handling complex scenarios including recurring subscriptions, milestone-based payments, and usage-based billing. It supports custom invoice formatting to meet specific customer needs, ensuring accuracy and timeliness in billing. This module not only improves cash flow but also elevates customer satisfaction through the delivery of precise and timely invoices.
Payments
This module simplifies the payment process by integrating with various payment gateways to accept diverse payment methods such as credit cards, Automated Clearing House (ACH) transfers, and checks. It automates the tracking of payment statuses, manages partial payments, and addresses exceptions like chargebacks. A customer portal feature provides visibility into invoices and enhances the payment experience. Automating these processes accelerates receivables collection, reduces manual reconciliation efforts, and improves cash flow management.
Revenue Recognition
Essential for compliance, the Revenue Recognition module automates the calculation of revenue based on contract terms, aligning with standards like ASC 606. It handles complexities such as deferred revenue and performance obligations, ensuring accurate and compliant financial reporting. This automation supports transparency and consistency in financial records, crucial for regulatory compliance and stakeholder trust.
Reporting
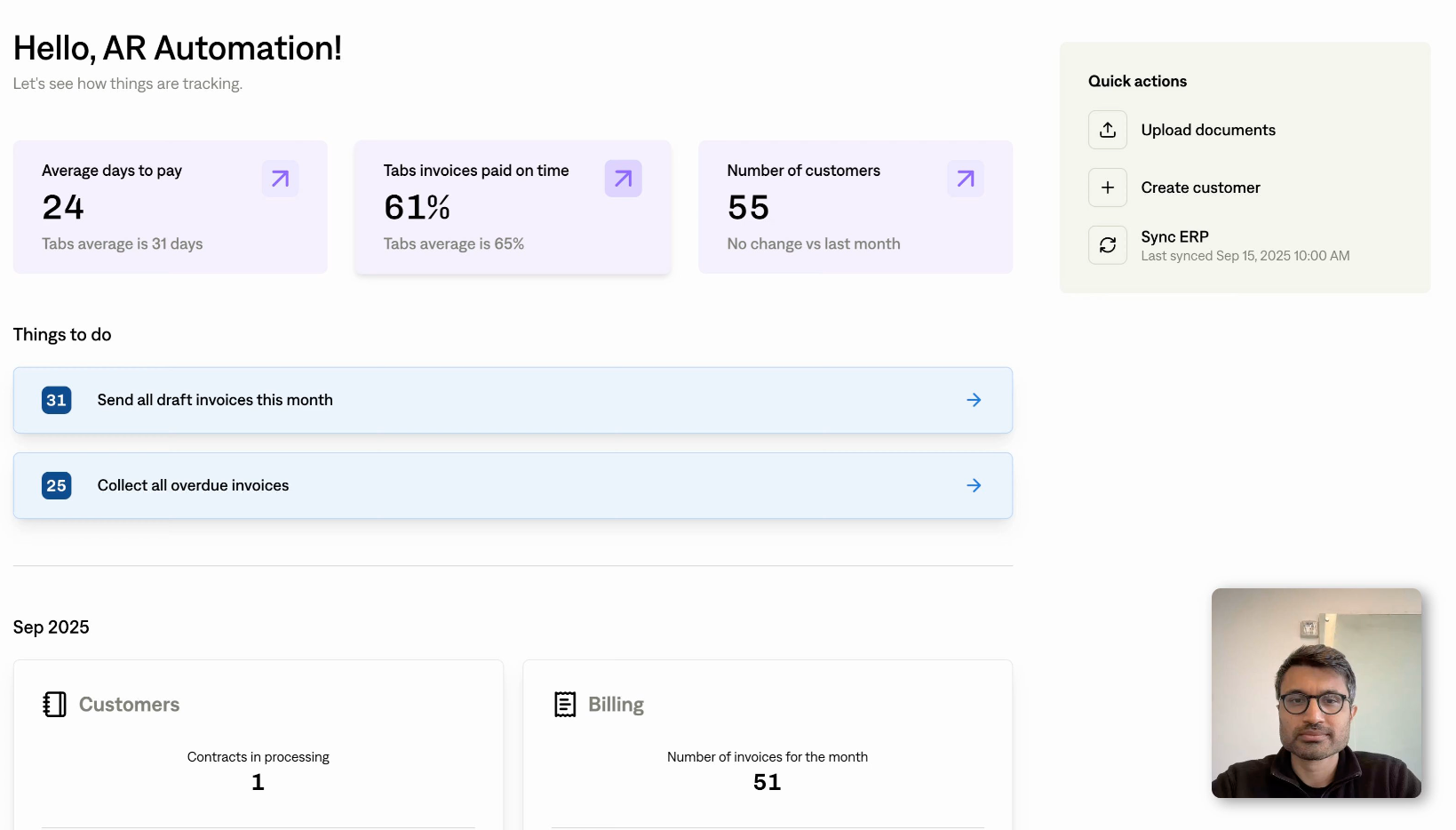
The Reporting module offers real-time insights and detailed analytics on key financial metrics such as revenue, annual recurring revenue (ARR), and cash flow. Customizable dashboards allow finance teams to monitor performance, identify trends, and make informed decisions. This module centralizes data reporting, eliminating the need for manual spreadsheets and enhancing the accuracy and timeliness of financial reports.
Integrations
This module ensures seamless connectivity between the RA platform and existing ERP systems, CRMs, and other business applications. It supports a variety of integrations through APIs and pre-built connectors, facilitating a smooth data flow across systems. This interoperability allows RA to enhance existing workflows rather than disrupt them, avoiding duplication of efforts and making it easier for businesses to adopt and leverage the benefits of the platform.
Data Aggregation
The data aggregation layer is the backbone of the RA platform, serving as a central repository that consolidates and organizes data from various sources. This layer ensures that all modules operate with consistent, up-to-date information, which enhances system efficiency and reliability. It provides a unified view of the revenue process, facilitating seamless interaction between modules such as Invoicing, Payments, and Revenue Recognition, and reduces the risk of errors associated with fragmented data sources.
This centralized view allows for interconnectedness between modules, enabling them to draw on the same underlying data to perform their tasks effectively. As a result, the platform not only streamlines data management but also minimizes the potential for errors and inconsistencies that often arise from siloed data.
Moreover, the data aggregation layer is crucial for enhancing data-driven decision-making. By structuring data across the revenue cycle, it enables advanced analytics and reporting capabilities that offer valuable insights into business performance. Finance teams can utilize these insights to identify trends, optimize processes, and make informed strategic decisions. Additionally, this layer supports compliance by ensuring that all relevant data is accurately captured and reported, adhering to regulatory requirements.
Overall, data aggregation empowers businesses to manage their revenue operations with increased precision, agility, and confidence, ensuring that strategic decisions are well-informed and operations are compliant and efficient.
How does RA differ from other similar or related technologies?
When evaluating tools to optimize operations, understanding how RA compares with other financial and revenue management software is crucial. While CRM systems, billing tools, AR software, general ledgers, and ERP systems play essential roles within a company, they typically focus on specific aspects of the revenue process and do not provide a comprehensive solution. This section explores the unique strengths and limitations of these software categories and demonstrates how RA complements and enhances their functionality, offering a more integrated approach to managing the entire revenue cycle.
RA vs. CRM Systems
Customer Relationship Management systems excel in managing and analyzing customer interactions throughout the customer lifecycle, focusing on sales, marketing, and customer service. While CRMs are adept at tracking customer data and nurturing relationships, they fall short in managing the complexities of the revenue process.
RA takes over where CRM systems end—post-deal closure. It automates the financial workflows that follow, such as invoicing, payment collection, and revenue recognition, ensuring that the financial aspects of customer relationships are managed with precision and efficiency. By integrating RA with a CRM, businesses can achieve a seamless transition from customer acquisition to revenue realization, with improved controls and reduced risk of errors.
RA vs. Billing Systems
Billing systems, often designed to handle specific billing types like recurring subscriptions or usage-based pricing, usually operate in isolation and cover only a fraction of the revenue cycle. In contrast, RA provides a holistic solution by integrating billing with other critical processes such as payments, revenue recognition, and financial reporting. This comprehensive approach allows businesses to manage their entire revenue process through a single platform, eliminating the need for disparate tools and enhancing overall efficiency and compliance.
AR Software
Accounts Receivable software focuses on tracking and managing the money owed to a business, essential for ensuring timely collections. However, AR software typically does not cover the full spectrum of revenue management. RA includes AR management within a broader system that also automates invoicing, revenue recognition, and reporting, thereby streamlining the entire revenue process and providing a unified approach to financial management.
General Ledger
The General Ledger (GL) is the backbone of a company’s accounting system, recording, categorizing, and summarizing all financial transactions. While the GL offers a comprehensive record of financial activity, it doesn't manage the operational processes that generate these transactions. RA fills this gap by automating the workflows that lead to revenue-related entries, such as invoicing and payments, ensuring accuracy, efficiency, and compliance. This integration results in a smoother financial close process and more reliable financial reporting.
The General Ledger (GL) is the core of a company’s accounting system, where all financial transactions are recorded, categorized, and summarized. While the GL provides a comprehensive record of all financial activity, it is not designed to manage the operational processes that lead to those financial entries. revenue automation fills this gap by automating the workflows that generate revenue-related transactions, such as invoicing, payments, and revenue recognition. RA ensures that these processes are accurate, efficient, and compliant, feeding precise data into the GL. This integration allows for a smoother financial close process and more accurate financial reporting, enhancing the overall reliability of the company’s financial data.
ERP Systems
Enterprise Resource Planning systems integrate various business operations into a unified system, managing a broad range of activities from finance to HR. While ERPs are effective at overseeing general business processes, they often lack the specificity required for detailed revenue management. RA enhances ERP systems by specifically targeting and automating the revenue cycle, including invoicing, payments, and reporting, thus optimizing the accuracy and efficiency of revenue operations while allowing businesses to leverage their existing ERP infrastructure.
What is life like for a company before and after implementing RA?
Before RA: Many businesses are bogged down by labor-intensive and error-prone manual processes to manage their revenue cycles. This traditional approach often leads to inefficiencies, inaccuracies, and delays.
After RA: Implementing RA revolutionizes these processes by automating crucial tasks, significantly reducing manual effort, and increasing accuracy throughout the revenue cycle.
Here's a closer look at the transformation across five key revenue-related processes.
1. Contract Review and Data Entry
Before: Finance teams manually review contracts to identify essential terms, billing schedules, and revenue recognition rules, then enter this data into systems manually—a process fraught with potential for errors and oversight.
After: RA automates contract ingestion and data extraction, populating the billing system directly with accurate information and dramatically reducing manual data entry and associated errors.
2. Complex Invoicing
Before: Manual calculations and custom invoice creation for complex billing arrangements like tiered pricing or usage-based billing are time-consuming and error-prone.
After: RA automates the entire invoicing process, using predefined rules and templates to ensure invoices are generated accurately and on schedule. Streamlined operations reduce administrative overhead.
3. Payment Tracking and Reconciliation
Before: Payment tracking and invoice reconciliation involve extensive manual work, including handling multiple spreadsheets and frequent communication with customers, which can delay cash flow and introduce discrepancies.
After: RA automates these processes, synchronizing payments with invoices in real-time, which speeds up reconciliation, enhances cash flow, and reduces errors. By eliminating the need for follow-ups, customer satisfaction is improved.
4. Revenue Recognition Calculations
Before: Revenue recognition requires meticulous manual calculations based on contract specifics, a process that's both complex and time-consuming, especially when complying with standards like ASC 606.
After: RA automates revenue recognition, applying appropriate rules based on the contract terms to ensure compliance and timely, accurate reporting, thus alleviating the manual burden and enhancing financial accuracy.
5. Financial Reporting and Analysis
Before: Financial reporting is typically a slow and error-prone process, heavily reliant on manual data compilation from various sources and extensive spreadsheet management.
After: RA offers real-time reporting capabilities, pulling data automatically into customizable dashboards and reports, which facilitates quicker, more reliable financial analysis and supports more informed decision-making.
Common Objections
1. "We already have an ERP system."
While ERP systems are integral for managing broad business operations, they often lack the specificity needed for complex revenue workflows like invoicing, revenue recognition, and ARR reporting. Revenue automation is designed to enhance, not replace, your existing ERP by automating and optimizing these intricate processes. RA works alongside your ERP to improve efficiency, accuracy, and scalability in revenue management—without requiring a complete system overhaul.
2. "Implementing RA sounds complex and time-consuming."
Implementing revenue automation is indeed a strategic investment but is structured to streamline operations significantly and save time overall. The process, supported by comprehensive guidance from RA providers—including steps like data migration, system integration, and training—ensures a smooth transition. The long-term benefits, such as quicker financial closes, reduced manual effort, and enhanced risk controls, far outweigh the initial setup time, making RA a valuable asset to your operations.
3. "Our billing and revenue processes are too unique."
Revenue automation platforms excel in their flexibility and adaptability to various business models and billing scenarios. Highly customizable, RA can be tailored to fit specific needs, whether you're dealing with subscription-based billing, usage-based pricing, or complex contract terms. This adaptability ensures that your unique billing and revenue processes are not just accommodated but optimized.
4. "We’re concerned about the cost of implementing."
The initial investment in revenue automation can be offset by the substantial long-term benefits it brings. RA reduces operational costs by automating labor-intensive tasks, minimizing errors, and improving cash flow management. Its scalability means it can grow with your business, preventing the future costs of manual adjustments or additional software. Over time, these savings and efficiency gains make RA a cost-effective solution for improving financial accuracy and operational productivity.
5. "We’re worried about disrupting our current processes."
Revenue automation is built to integrate seamlessly with your existing systems, minimizing any disruption to your operations. RA platforms offer diverse integration options, such as APIs and pre-built connectors, ensuring smooth data flow between your ERP, CRM, and other business applications. The careful management of the implementation process, coupled with close collaboration with your team, means RA will enhance rather than disrupt your current workflows, leading to a more efficient and streamlined revenue management process that leverages the strengths of your existing systems.
Getting started
Implementing revenue automation software requires a strategic, three-step approach to transition from manual to automated revenue processes effectively. This structured method—Assess, Implement, and Optimize—ensures businesses thoroughly evaluate their current operations, deploy the appropriate RA platform, and continually refine their systems to enhance efficiency and scalability. This approach not only simplifies the adoption of RA but also maximizes its benefits for improved revenue management.
Step 1: Assess Current Revenue Workflows
The first step is a comprehensive assessment of your existing revenue processes. This step involves mapping the entire revenue cycle from contract initiation to financial reporting and identifying manual, inefficient, or error-prone areas. Involving key stakeholders from finance, accounting, sales, and operations is crucial to ensure a holistic review of all relevant processes. The objective is to pinpoint where automation can significantly impact, such as in invoicing, payment processing, revenue recognition, or reporting.
Identifying these pain points allows you to target critical areas for automation first, tailor-making the RA implementation to meet your most pressing needs.
Step 2: Implement
With a clear understanding of current processes, the next step is to implement the RA platform. This phase involves selecting an RA solution that fits your business requirements and integrates seamlessly with existing systems like ERP, CRM, and billing software. Implementation starts with setting up essential modules—Data Capture, Invoicing, Payments—and customizing them to meet your specific business needs.
Close collaboration with your RA provider is vital during this stage to ensure smooth setup, including data migration, integration testing, and user training. This foundational phase prepares your RA platform to automate and streamline your revenue processes efficiently.
Step 3: Optimize and Scale
Once the RA platform is operational, the emphasis shifts to optimization and scaling to leverage the full potential of the solution. Optimization entails continuous monitoring of the RA system, soliciting user feedback, and adjusting the setup to boost efficiency and accuracy. This may involve refining automation rules, enhancing reporting functions, or adding new modules as business requirements evolve.
As your business grows, the RA platform is designed to scale accordingly, managing larger transaction volumes, more complex billing scenarios, and new revenue models. Regularly revisiting and refining your RA configuration ensures the platform remains valuable, fostering ongoing improvements in revenue management.
Looking forward
The future of revenue automation is on a rapid evolutionary path as businesses increasingly seek to enhance efficiency, accuracy, and scalability in their revenue management processes. With ongoing technological advancements, RA is set to integrate more deeply with cutting-edge technologies such as AI and Machine Learning (ML). This integration will enable predictive analytics and intelligent decision-making, allowing RA platforms to not only automate current processes but also proactively identify potential issues, optimize revenue streams in real-time, and provide strategic insights that propel business growth. The capability to forecast revenue outcomes and manage financial risks proactively will render RA an essential tool for businesses across various sizes and industries.
Another significant trend shaping the future of RA is the growing need for seamless integration across all business systems. As organizations expand their digital toolsets, the demand for RA platforms that can effortlessly connect with ERP systems, CRM platforms, and other business applications is increasing. This move towards greater interoperability is expected to position RA platforms as the central hubs of financial operations, consolidating data from diverse sources and offering a unified view of the entire revenue lifecycle. Enhanced integration will improve data accuracy, ensure compliance, and facilitate a more holistic approach to financial management.
Looking further ahead, RA’s role in supporting innovative business models is set to become even more crucial. As companies venture into new revenue avenues, such as subscription-based services, usage-based pricing, and digital-first offerings, RA platforms will need to evolve to offer the necessary flexibility to manage these dynamic models effectively. The future of RA will feature enhanced customization and adaptability, empowering businesses to explore and scale new revenue strategies without the limitations imposed by traditional financial systems.
Ultimately, revenue automation software is poised to become a fundamental component of modern business operations, equipping companies to confidently tackle the complexities of the digital economy.
Conclusion
Navigating the complexities of the digital economy requires robust and precise revenue management strategies. RA software provides a compelling solution to the challenges faced by many businesses in managing their revenue cycles effectively. By automating critical processes such as invoicing, payments, revenue recognition, and reporting, RA not only boosts operational efficiency but also ensures adherence to evolving accounting standards. Its adaptability and scalability render it indispensable for businesses of all sizes, allowing them to swiftly adapt to market shifts and confidently explore new revenue models.
This guide has highlighted the extensive benefits of implementing RA, from minimizing manual errors and enhancing cash flow to offering actionable insights that inform strategic decisions. We have delineated RA’s advantages over other software solutions, provided a roadmap for its implementation and optimization, and discussed its promising future fueled by advancements in AI, machine learning, and improved integrations. As RA progresses, it is set to become a crucial element in securing a competitive advantage in a complex financial environment.
In essence, revenue automation is more than a mere technological enhancement; it is a strategic necessity for any business aiming to succeed in today’s economy. By adopting RA, companies can refine their revenue operations, cut costs, and unlock new growth opportunities. The insights and strategies presented in this guide will serve as a comprehensive resource to help you fully leverage the potential of revenue automation and ensure your business’s long-term prosperity. Now is the time to act. With revenue automation, you can transform your revenue management processes and achieve a level of operational efficiency and precision that distinguishes your business in the marketplace.